Musical Instrument Repairers and Tuners
Where Would You Like to Go Next?
Or, Explore This Profession in Greater Detail...
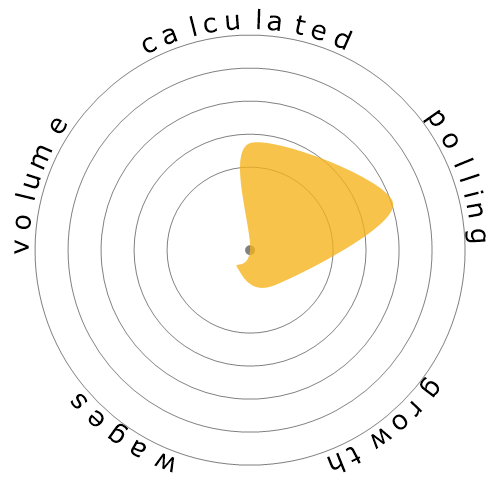

What does this snowflake show?
What's this?
We rate jobs using four factors. These are:
- Chance of being automated
- Job growth
- Wages
- Volume of available positions
These are some key things to think about when job hunting.
People also viewed
Calculated automation risk
Moderate Risk (41-60%): Occupations with a moderate risk of automation usually involve routine tasks but still require some human judgment and interaction.
More information on what this score is, and how it is calculated is available here.
User poll
Our visitors have voted there's a low chance this occupation will be automated. However, the automation risk level we have generated suggests a higher chance of automation: 54% chance of automation.
What do you think the risk of automation is?
What is the likelihood that Musical Instrument Repairers and Tuners will be replaced by robots or artificial intelligence within the next 20 years?
Growth
The number of 'Musical Instrument Repairers and Tuners' job openings is expected to rise 1.5% by 2033
Total employment, and estimated job openings
Updated projections are due 09-2025.
Wages
In 2023, the median annual wage for 'Musical Instrument Repairers and Tuners' was $42,800, or $21 per hour
'Musical Instrument Repairers and Tuners' were paid 10.9% lower than the national median wage, which stood at $48,060
Wages over time
Volume
As of 2023 there were 6,170 people employed as 'Musical Instrument Repairers and Tuners' within the United States.
This represents around < 0.001% of the employed workforce across the country
Put another way, around 1 in 24 thousand people are employed as 'Musical Instrument Repairers and Tuners'.
Job description
Repair percussion, stringed, reed, or wind instruments. May specialize in one area, such as piano tuning.
SOC Code: 49-9063.00
Comments (3)
In general, this kind of work is much like sculpting in wood; the material differs greatly from case to case - and very often, one improper move can break the instrument you're repairing even worse.
The difference between "proper" and "improper" is something only your experience and touch can tell you. It's next to impossible to describe it in concrete terms, not to mention - to transform it into an algorithm.
Reply to comment